BOOK AN APPOINTMENT
Prices
Contact
Open Hours
Vaccines
Destinations
Cholera
Cotham Pharmacy
Cholera
Cholera is an acute diarrhoeal infection caused by ingestion of food or water contaminated with the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. Approximately 1 - 4 million cases occur globally each year.
 Transmission
Transmission
- Cholera is transmitted through the faecal-oral route, by ingestion of faecally contaminated water and occasionally foodstuffs, particularly shellfish.
- Transmission is closely linked to inadequate environmental management where minimum requirements of clean water and sanitation are not met.
- Humans are the only known hosts.
- Bacteria can survive for weeks to months in water.
- High infecting dose required to cause disease.
 Vaccine Schedule
Vaccine Schedule
| Age | Primary Schedule | Booster |
|---|---|---|
| 2 years + | 2 dose on Day 0, 1-6 weeks | 2 years |
 Transmission
Transmission
Reported from all world regions.
Two serogroups of V. cholerae are responsible for outbreaks, 01 (found worldwide) and 0139 (confined to SE Asia); 01 is responsible for most recent outbreaks.
Recently new variant strains have been seen in Africa and Asia which are thought to be causing more severe cholera with higher case fatality rates.
Epidemics likely to occur where sanitation and water systems are disrupted or inadequate e.g. urban slums, refugee camps and following natural disasters and floods.
 Signs and Symptoms
Signs and Symptoms
- 75% infected will be asymptomatic.
- 80% symptomatic have mild - moderate diarrhoea.
- 20% - acute watery diarrhoea (rice water stool) +/- vomiting.
- May lose ~ 30 litres fluid in 24 hours, resulting in profound dehydration and death.
- Fever, abdominal pain unusual.
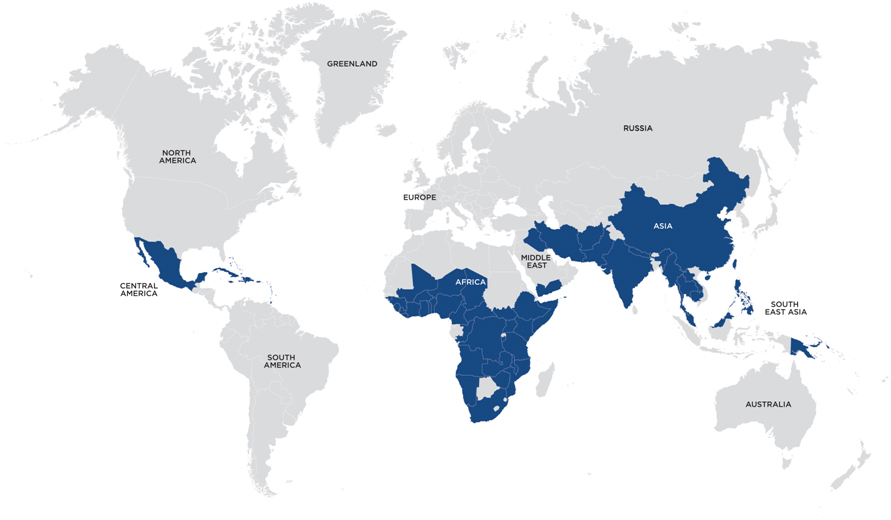
 RISK AREA MAP - CHOLERA
RISK AREA MAP - CHOLERA
CONTACT
3-5 Cotham Hill,
Bristol
Bristol
BS6 6LD
Bristol
Bristol
BS6 6LD
Contact Us
0117 973 6580
INFORMATION
Company Registration:
08064580
Premises GPhC Number:
1028606
Superintendent
Anand Shah
OPENING HOURS